Geography & Nature of Vietnam
Explore Vietnam from North to South
Stretching over 1,650 kilometers from north to south, Vietnam is a country of dramatic landscapes, diverse ecosystems, and remarkable natural contrasts. From snow-dusted mountain peaks in the far north to tropical islands in the south, Vietnam’s geography shapes not only its scenery but also its culture, climate, and biodiversity.
This overview introduces Vietnam’s natural regions from North to South, highlighting key landscapes, ecosystems, and environmental features. Detailed guides will be available soon.
I. Northern Vietnam – Mountains, Karst & Four Seasons
Northern Vietnam is known for its rugged mountains, limestone formations, and the most distinct seasonal variation in the country.
1. Northwest Highlands
Home to Vietnam’s highest peaks, including Fansipan (3,143 m), the northwest features dramatic mountain ranges, terraced rice fields, and deep valleys.
- Snow and frost can occur in winter at high elevations (especially around Sa Pa)
- Cool summers, cold winters
- Rich ethnic minority cultures
- Dense forests and high biodiversity
👉 Mountain landscapes & trekking routes (Coming Soon)
👉 Northern highland climate guide (Coming Soon)
2. Northeast & Karst Landscapes
This region is famous for spectacular limestone formations and UNESCO-recognized natural wonders.
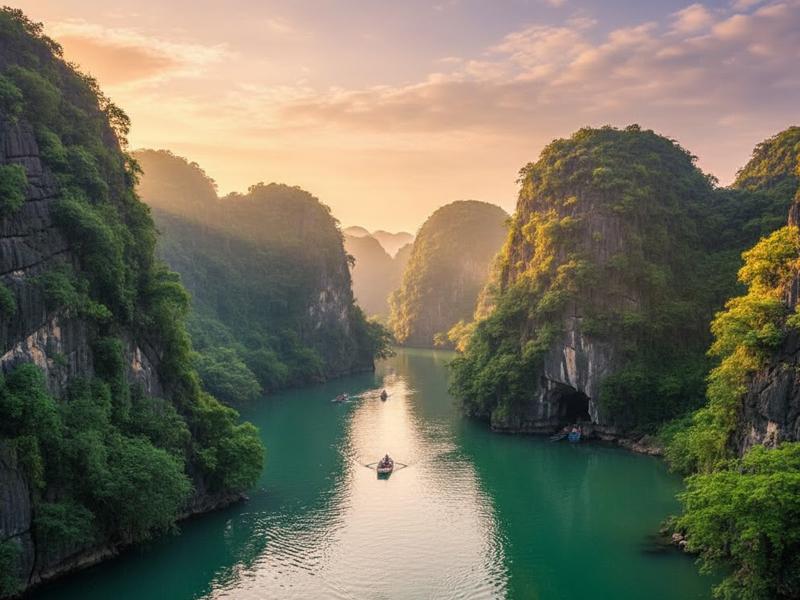

- Ha Long Bay – iconic limestone karsts rising from emerald waters
- Phong Nha-Ke Bang National Park – vast cave systems and underground rivers
The terrain here is shaped by millions of years of geological evolution, creating one of Southeast Asia’s most impressive karst landscapes.
👉 National Parks of Vietnam (Coming Soon)
👉 Limestone & cave systems explained (Coming Soon)
3. Red River Delta
The fertile plains surrounding Hanoi form the cultural and agricultural heart of the north.
- Humid subtropical climate
- Four distinct seasons
- Drizzle and damp conditions (mưa phùn) from February to April
- Dense river network
Winter temperatures in mountainous areas can fall below 0°C, whereas summer heat in the Red River Delta frequently surpasses 35°C. In dense urban areas like Hanoi, the urban heat island effect can intensify extreme heat. During severe heatwaves — especially when dry foehn winds (locally known as gió phơn or gió Lào) combine with urban heat retention — outdoor temperatures have been recorded at around 42–43°C, with perceived temperatures even higher.
👉 Northern weather & temperature by month (Coming Soon)
II. Central Vietnam – Mountains, Passes & Coastlines
Central Vietnam is geographically narrow yet incredibly diverse, squeezed between the mountains and the sea.
1. The Annamite Range (Trường Sơn Mountains)
Running along the western border, this mountain chain separates Vietnam from Laos and shapes rainfall patterns across the country.
- Tropical forests
- High biodiversity
- Important wildlife corridors
2. Central Coast
Stretching from Thanh Hoa to Binh Thuan, this region features:
- Long sandy beaches
- Coastal lagoons
- Dramatic mountain passes like Hai Van Pass
Cities such as Da Nang sit between mountains and sea, offering a striking geographical contrast.
The climate here differs from the north:
- Hot and dry season (often influenced by hot winds)
- Heavy rainfall and typhoons from September to November
👉 Central Vietnam climate guide (Coming Soon)
👉 Coastal landscapes & beaches (Coming Soon)
III. Southern Vietnam – Tropics, Rivers & Islands
Southern Vietnam is characterized by flat terrain, tropical warmth, and vast waterways.
1. Central Highlands (Tây Nguyên)
A plateau region known for:
- Volcanic soil
- Coffee plantations
- Waterfalls and pine forests
Cities like Da Lat enjoy cooler temperatures due to elevation, creating a “temperate island” within tropical Vietnam.
2. Mekong Delta
The southernmost region is shaped by the mighty Mekong River.
- Fertile floodplains
- Floating markets
- Dense canal systems
This region experiences:
- Consistently warm temperatures year-round
- Distinct wet (May–November) and dry (December–April) seasons
3. Southern Islands
Vietnam’s southern waters are home to tropical islands such as Phu Quoc, known for:
- Coral reefs
- Marine biodiversity
- White sand beaches
👉 Island ecosystems & marine life (Coming Soon)
Climate Diversity Across Vietnam
Vietnam spans multiple climate zones:
- Humid subtropical (North) – 4 seasons, winter cold possible
- Tropical monsoon (Central & South) – hot temperatures, seasonal rains
- Highland temperate zones – cooler year-round conditions
From snow in the northern mountains to tropical sunshine in the south, Vietnam offers remarkable climatic contrast within a single country.
👉 Monthly temperature & rainfall tables (Coming Soon)
Biodiversity & Environmental Significance
Vietnam is recognized as one of the world’s biodiversity hotspots:
- Over 16 national parks
- Rare and endemic species
- Mangroves, coral reefs, tropical forests
Conservation plays a crucial role in protecting these ecosystems for future generations.
👉 Full list of National Parks (Coming Soon)
👉 Wildlife & conservation efforts (Coming Soon)
Conclusion
From the towering peaks of the north to the fertile Mekong Delta in the south, Vietnam’s geography is as diverse as its culture. Mountains, rivers, forests, and seas come together to create a country rich in natural beauty and ecological significance.
Whether you are trekking in highlands, cruising through limestone bays, or relaxing on tropical beaches, Vietnam’s geography offers endless opportunities to explore and connect with nature.